Secure IoT Remote Management: Best Practices & Insights
In an era where the Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly transforming industries, is your organization adequately equipped to safeguard its IoT devices against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats?
This article offers a comprehensive guide to navigating the complex world of secure remote management for IoT devices. It's a critical subject, as the proliferation of connected devices presents both unprecedented opportunities and significant security challenges. As IoT continues its exponential growth, from smart homes and wearables to industrial machinery and critical infrastructure, the necessity of robust security measures becomes increasingly apparent. This guide provides practical advice and actionable steps to protect your network.
Before delving into specifics, it's crucial to acknowledge the fundamental principle: a strong security posture begins with well-defined company policies specifically tailored for IoT devices. These policies serve as the cornerstone of a secure IoT environment, dictating how security is deployed, managed, and enforced. They define authorized personnel, approved communication channels, and permissible operational windows. Without these foundational policies, your IoT deployments are essentially operating without a safety net, vulnerable to a range of potential exploits.
- Vega Movie Watch Online Safer Alternatives To Vegamovies
- Indian Cinema Streaming Guide Explore Movies Shows Justwatch More
Let's move to the table below:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Security Policy Framework | Defines rules for IoT device deployment, access, and management. |
| Authorized Personnel | Specifies who has permissions to interact with and manage IoT devices. |
| Communication Channels | Outlines approved methods for accessing and controlling devices (e.g., VPN, SSH). |
| Operational Windows | Sets the times when devices are accessible and when specific management tasks are permitted. |
| Encryption Protocols | Mandates use of strong encryption like TLS/DTLS for all network traffic. |
| Firewall Configuration | Recommends detailed configuration of firewalls to restrict traffic and deny unauthorized access. |
| Regular Audits | Suggests periodic security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities. |
| Incident Response Plan | Requires a plan to mitigate damage and recover from security breaches, and data loss incidents. |
| Employee Training | Requires all employees should be educated on security risks and best practices in IoT devices |
| Device Hardening | Advocates that you should implement this by disabling unused services and other default settings |
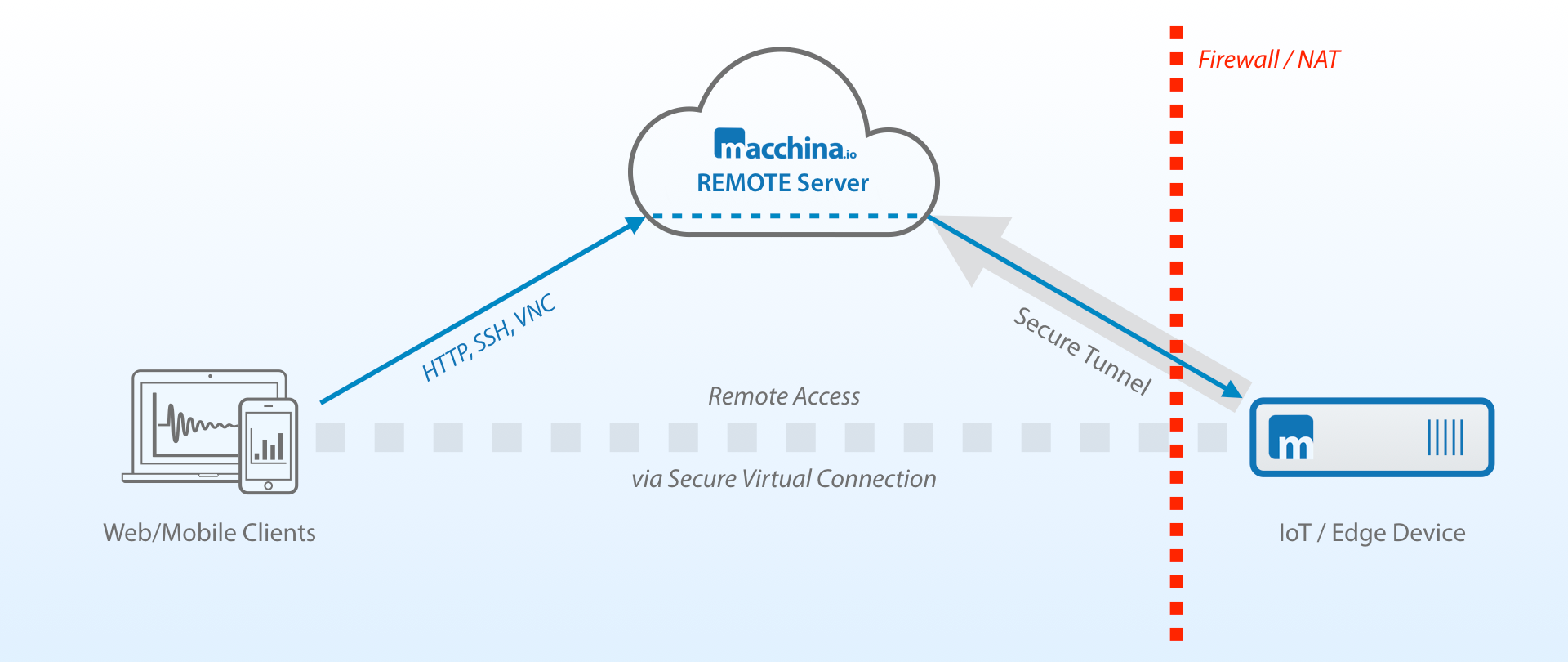
One of the most effective ways to connect and manage devices from anywhere is through RemoteIoT. This technology extends its reach even to devices concealed behind firewalls. A key feature of RemoteIoT is its reliance on SSH tunnels for secure data transmission. This means all network traffic is encrypted, preventing unauthorized access. The data within the tunnel is inaccessible, even to RemoteIoT itself, providing an additional layer of security.
An important element of effective IoT device management is the integration of remote control functionalities with robust monitoring capabilities. This combined approach allows for proactive device management. By enabling remote access, administrators can troubleshoot issues, update firmware, and reboot devices as needed. Simultaneously, monitoring tools provide real-time insights into device health, login attempts, and resource usage, all without requiring physical presence at the device location.
- Movierulz Kannada Movies Latest Updates Streaming Guide 20242025
- Is Hdhub4ukids Safe A Guide For Parents Alternatives
The question of implementation is a core concern. How do you implement remote IoT device management, and what tools are used? The answer lies in a combination of strategies. First, carefully select Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools to track key metrics like device health, login attempts, and resource consumption. Then, to ensure a secure transition to new technologies, always prioritize encrypted connections, ideally using protocols like TLS or DTLS. Correctly configuring firewalls and employing VPN connections for remote access provide an additional level of protection.
The benefits of remote device management are numerous. It streamlines the management of devices at scale, which leads to increased operational efficiency. Remote management allows you to manage multiple devices simultaneously. Centralized management platforms also offer a simplified view of your entire IoT infrastructure, making it easier to identify and address issues. This improves the performance of your whole system.
Removing remote device management, is the reverse of setup and configuration, and it will require you to unenroll the device from its management software, potentially requiring access credentials for proper authorization.
It is well known that IoT device management is not without its challenges. One must carefully consider the potential pitfalls of remote control practices in the initial stages of implementation. These can include unauthorized access, data breaches, and operational disruptions. It is essential to have a comprehensive plan in place to deal with any difficulties that may arise.
When dealing with large IoT deployments, a centralized approach becomes a necessity. From a central dashboard, administrators can monitor, manage, and update a multitude of devices. This centralized system will improve operational efficiency and reduce risks.
A key component of this centralized management is the use of a dedicated IoT device management platform. Such a platform must provide secure, remote access from a dashboard and facilitate automation, security management, mass firmware updates, and real-time notifications for breaches or specific conditions.
In today's interconnected world, every device, machine, and controller can be a target for attackers. Given that many devices were not designed with security in mind, traditional methods don't always work. A significant increase in IoT malware attacks, along with the rise of malicious payloads, necessitates a new approach to security.
| Best Practices | Details |
|---|---|
| Security Policy | Establish and enforce policies for device security, access control, and data protection. |
| Encryption | Use strong encryption (TLS/DTLS) for all network traffic. |
| Firewall | Configure firewalls to restrict traffic. |
| VPN | Use VPN connections for secure remote access. |
| RMM Tools | Implement remote monitoring and management tools. |
| Regular Audits | Conduct security audits and penetration testing. |
| Access Control | Implement access control and multi-factor authentication (MFA). |
| Firmware Updates | Implement secure firmware updates. |
| Incident Response | Have an incident response plan. |
The use of secure tunneling, a key feature of AWS IoT device management, is worth noting. This enables customers to access remote devices over a secure connection managed by AWS IoT. Secure tunneling does not require any changes to your existing inbound firewall rules, thus maintaining the same level of security.
There are a number of tools available, with features ranging from the Teamviewer IoT, known for its user-friendly interface and scripting for automation, to comprehensive platforms offering terminal access, app control, and edge management.
In conclusion, the secure remote management of IoT devices is not just a technical requirement. It's a critical factor for maintaining operational integrity, ensuring data security, and protecting your business from evolving threats. By adopting a proactive and comprehensive approach, businesses can harness the power of IoT while mitigating the associated risks.
Article Recommendations
- Get Your Watch On Movies Anywhere Hd Hub 4u Options
- Ullu Web Series Watch Download Guide 2024 Legal Safe

Detail Author:
- Name : Ms. Eveline Funk
- Username : hilbert85
- Email : cboehm@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 2007-04-09
- Address : 652 Walsh Lodge Suite 151 New Marjoriebury, NM 55987
- Phone : (443) 493-7338
- Company : Adams and Sons
- Job : Pump Operators
- Bio : Et sint iusto mollitia sed. Atque ad sint et provident quo. Dolorem doloremque animi sint reiciendis. Nam vero illo facilis dolores molestiae.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@joanie.jast
- username : joanie.jast
- bio : Enim eveniet et eius aliquid non.
- followers : 1656
- following : 2542
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/joaniejast
- username : joaniejast
- bio : Ad sit ipsam nam iste quo itaque.
- followers : 1369
- following : 713
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/jast1996
- username : jast1996
- bio : Nulla beatae enim aperiam. Nam rem nesciunt minus. Itaque occaecati dolor quo libero. Eum dolores delectus quo blanditiis et eos.
- followers : 6709
- following : 780
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/joanie_id
- username : joanie_id
- bio : Voluptatibus culpa ut ipsum quis ea doloribus eum. Ipsum harum enim enim aut voluptas ut eos.
- followers : 1047
- following : 205